- UK scientists (Prof. Glenn Gibson, Dr. Gemma Walton, Dr. Kirsty Hunter and Prof. Tim Spector) requested that Matt Hancock (the country’s health secretary) call attention to the links between gut health and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). (The original content of the letter was not located)
- Via the lung-gut pathway, research suggests a relationship between immunity to COVID-19, the respiratory tract and the gut microbiome.1
- While most COVID patients present with primarily respiratory symptoms, some manifest gastrointestinal symptoms including vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain. Viral RNA has been recovered from the stool in those infected as well as a high level of viral receptor angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in gastrointestinal epithelial cells.2
- Probiotics (Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bacillus subtilis, and Enterococcus faecalis) demonstrated significantly less ventilator-associated pneumonia compared with placebo.3, 4
- Glyphosate-based herbicides have been shown to impair the microbiota via the shikimate pathway. 5, 6
- “It is likely that a novel and more targeted approach to modulation of gut microbiota as one of the therapeutic approaches of COVID-19 and its co-morbidities will be necessary.”7
There is an erratic progression and presentation of illnesses from COVID-19 from the global perspective. While some countries have leveled off and are lessening restrictions, others like the US continue to spike and have taken the lead in the number of global cases. The graph below depicts this comparison between the US and other countries:

(https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/data/new-cases)
While the scientific community scurries to find solutions to treating this newly emergent virus, such as a COVID-19 vaccine, the elephant in the room to be addressed is why is the US surging in the number of cases while many other countries have leveled off or are declining in numbers?
The Role of the Microbiota
Over the past decade, the microbiota has become front and center in understanding their role in human health. This collection of organisms, mostly centered in the large intestine, are key modulators of immunity. The development of the human microbiome begins in preconception and the baby inherits these vital microbes which will form their own microbial community from a vaginal birth and subsequent breastfeeding. The microbiota then begins the task of the development of the innate immune system while the baby receives assistance in adaptive immunity with antibodies donated from mom in the breast milk until they are able to produce their own. The gastrointestinal immune system is one of the most extensive networks in the body. Although the role of microbes (such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium) and how they regulate this immune function has been established, there is a complex orchestration of microbial-immune crosstalk that is just beginning to be unraveled.8 There are many modern day challenges to the healthy establishment, maintenance and nourishment of the microbiota and one of the biggest challenges are antibiotics which will be addressed further below.
A Quick Look at Immunity
It has been well-established at this juncture that the array of symptoms produced by COVID-19 include a vast spectrum of findings from asymptomatic states, to mild viral symptoms, pneumonias of varying severity and death. A key modulator of poor outcomes includes the release of inflammatory cytokines causing a “cytokine storm” with overwhelming inflammation. This aggressive immune response has been a target of treatment in terms of using immunosuppressants such as steroids to squelch this response.9 Recent data is showing that those patents with more severe disease and worse outcomes have lower levels of CD8+T cells.
T cells are a type of white blood cell that is a central part of immune defense and there are 4 different types. Two types that have shown to be extremely important in COVID-19 infection includes CD8+ cells which are tasked in destroying pathogens such as viruses, and CD4+ cells, which are helper T cells because they stimulate immune responsiveness. (The CD4/CD8 ratio is one of the lab tests to assess immune function in an individual.) Recent studies are showing that the number of CD8+ and NK (Natural Killer) cells are exhausted in COVID-19 patients and increased numbers are demonstrated with recovery.10 It has been well established in the literature that the microbiota composition can regulate virus-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells as well as antibody responses following influenza viral infections. Of note, following influenza infection, immune activation of certain cells led to regulation of immunity in the respiratory tract as well, supporting the role of the “lung-gut pathway”.11 This study as well as others highlight the importance of the relationship between the gut microbiota, the respiratory tract and viral infections.1, 11 Another important finding from the work of Dr. Iwasaki and colleagues, published at Yale University, is that immune responses to respiratory influenza virus infection were diminished by antibiotic treatment. While the paper goes into great detail regarding different antibiotics and their effects on various microbes, for sake of brevity, two key points can be derived from their findings. Viral infections effect both intestinal and lung immune health via the gut-lung pathway and antibiotics diminished immune function, which predisposed the mice to high viral replication in the lung.
What is the role of glyphosate?
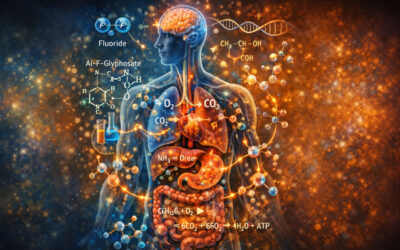
We can extrapolate that the gut microbiota could also be playing a major role in modulating the immune response in COVID-19. A pictorial demonstration of what that may look like is demonstrated here: 12

In order to maintain a robust gut microbiota, a key strategy is removal of substances that are detrimental to microbiota such as unintended antibiotics. This is where the understanding of the mechanism of action is vital to supporting microbiota welfare. Glyphosate has been patented as an antibiotic by Monsanto/Bayer.13 Numerous studies have now identified the mechanism of action of glyphosate on the microbiota as well as the subsequent microbial outcomes.14 Glyphosate decreases beneficial bacterial while assisting the growth of pathogens such as clostridial species.15 These imbalances in the microbiota have profound effects on the health of children such as ASD as well as livestock. 16, 17 Considering the fact that the average daily diet of most Americans is abundant in glyphosate as well as other pesticides and nutrient deficient (from soil depletion), one can appreciate that chronic dosing of glyphosate will result in an underperforming immune system which is unable to meet the challenges of modern day infections.
In order to be able to handle new infections such as COVID-19, supporting the microbiota and hence, the gut-lung pathway, an initial step would be to clean and disencumber the physiologic terrain.
“Germs seek their natural habitat – diseased tissue – rather than being the cause of diseased tissue.” – Antoine Béchamp 18

Our most valuable asset, our children, exhibit higher levels of glyphosate in biofluids than adults.19 In understanding the relationship of chemical contaminants such as glyphosate on the microbiota and how it ultimately effects our immunity and other physiologic pathways, the larger looming question posed is are we willing to accept this toxic injury to our children and our environment?
References
- Enaud R, et al. The Gut-Lung Axis in Health and Respiratory Diseases: A Place for Inter-Organ and Inter-Kingdom Crosstalks: Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 19 February 2020 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00009
- Sung J, et al. Covid‐19 and the digestive system; JGH; 25 March 2020 https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.15047
- Guan WJ, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China; N Engl J Med; 2020; published online Feb 28. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032.
- Chen N, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet 395: 507–13
- Message R, et al. Shotgun metagenomics and metabolomics reveal glyphosate alters the gut microbiome of Sprague-Dawley rats by inhibiting the shikimate pathway; BioRxiv; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/870105
- https://gmoscience.org//glyphosate-and-roundup-disrupt-the-gut-microbiome-by-inhibiting-the-shikimate-pathway; Jan. 15, 2020
- Mak J, et al. Probiotics and COVID-19: one size does not fit all; Published Online; April 24, 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/ S2468-1253(20)30122-9
- Malloy K, Ahern P. Understanding immune–microbiota interactions in the intestine; Immunology; 27 November 2019 https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13150
- Hadfield R, et al. Inhaled corticosteroids and COVID-19: a systematic review and clinical perspective; European Respiratory Journal 2020; doi: 10.1183/13993003.01009-2020
- Tian Z, et al. Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients; Cellular and Molecular Immunology; 17, 533-535(2020)
- Iwasaki A, et al. Microbiota regulates immune defense against respiratory tract influenza A virus infection; PNAS; March 29, 2011 108 (13) 5354-5359; https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1019378108
- Mohanty A. Dhar D. Gut microbiota and Covid-19- possible link and implications; Virus Research; Vol 285, Aug 2020, 198018
- https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/86/6d/8e/2d98b85f6574ef/US7771736.pdf
- Ibid 5
- Shehata A., et al.
- The Effect of Glyphosate on Potential Pathogens and Beneficial Members of Poultry Microbiota In Vitro; Curr Microbiol; DOI 10.1007/s00284-012-0277-2
- Li Q., et al. The Gut Microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorders; Front. Cell. Neurosci., 28 April 2017 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00120
- Obiturary Professor Bechamp. Br Med J; 1908;1:1150; https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.1.2471.1150-b
- Gillezeau C., et al. he evidence of human exposure to glyphosate: a review; Environ Health. 2019; 18: 2l Published online 2019 Jan 7. doi: 10.1186/s12940-018-0435-5